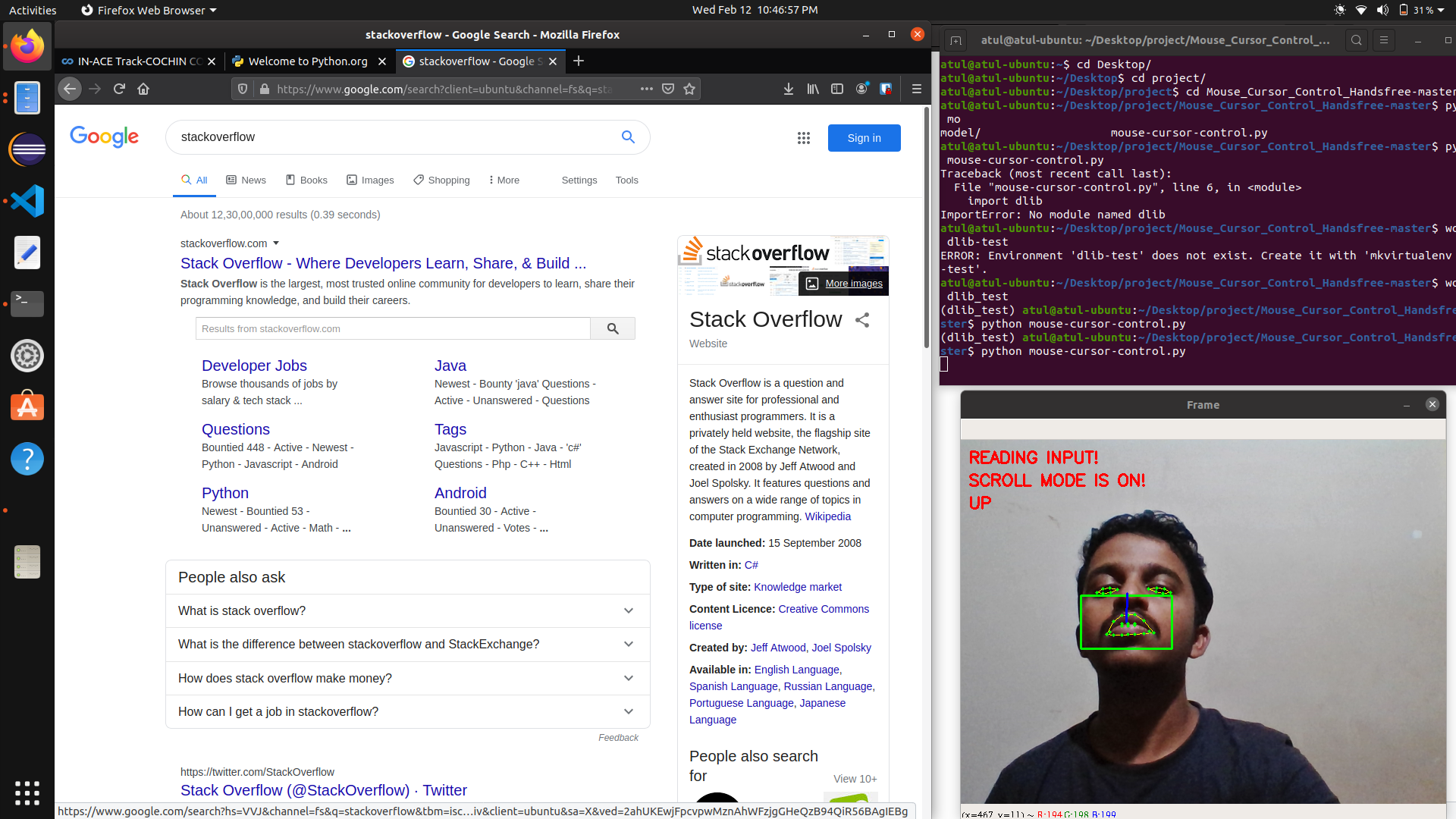
Human-computer interaction (HCI) is a multidisciplinary field of study focusing on the design of computer technology and, in particular, the interaction between humans (the users) and computers. While initially concerned with computers, HCI has since expanded to cover almost all forms of information technology design, Below video shows how we build it.
This idea shows that how a disabled person can make interaction between a computer and the user should resemble a human-to-human, open-ended dialogue. Initially, HCI researchers focused on improving the usability of desktop computers (i.e., practitioners concentrated on how easy computers are to learn and use). However, with the rise of technologies such as the Internet and the smartphone, computer use would increasingly move away from the desktop to embrace the mobile world. Also, HCI has steadily encompassed more fields. Human-computer interaction (HCI) is about understanding what it means to be a user of a computer (which is more complicated than it sounds), and therefore how to create related products and services that work seamlessly. It’s an important skill to master, because it gives any company the perspective and knowledge needed to build products that work more efficiently and therefore sell better.
If you are still looking for that one person who will change your life, take a look in the mirror.
“…it no longer makes sense to regard HCI as a specialty of computer science; HCI has grown to be broader, larger and much more diverse than computer science itself. HCI expanded from its initial focus on individual and generic user behavior to include social and organizational computing, accessibility for the elderly, the cognitively and physically impaired, and for all people, and for the widest possible spectrum of human experiences and activities. It expanded from desktop office applications to include games, learning and education, commerce, health and medical applications, emergency planning and response, and systems to support collaboration and community. It expanded from early graphical user interfaces to include myriad interaction techniques and devices, multi-modal interactions, tool support for model-based user interface specification, and a host of emerging ubiquitous, handheld and context-aware interactions.”